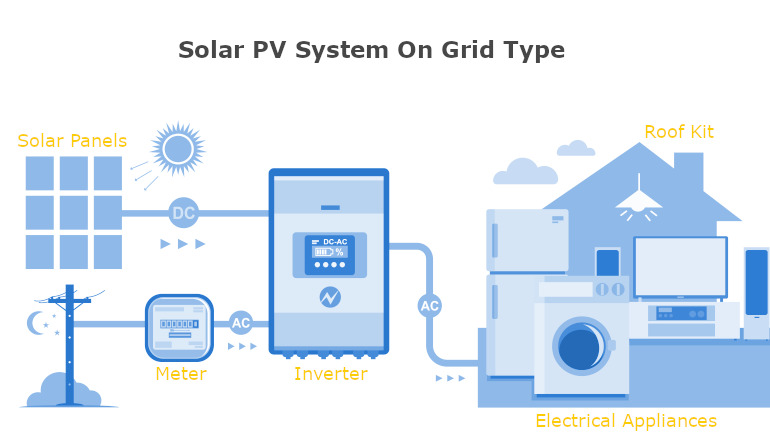
How Solar PV Works!
Solar PV (Photovoltaic) systems convert sunlight directly into electricity using photovoltaic cells. Here is how it works:
1. The photovoltaic cells are made up of semiconducting materials, usually silicon, which have special properties that allow them to absorb photons (particles of light) and release electrons.
2. When sunlight strikes the cells, the photons are absorbed by the semiconductor material, which causes the electrons in the material to become excited and move around.
3. The movement of the electrons creates a flow of electricity that can be collected by wiring the cells together in a solar panel.
4. The electricity produced by the solar panel is direct current (DC), which needs to be converted into alternating current (AC) in order to be used in homes and businesses. This is done by an inverter.
5. The AC electricity can then be used to power homes, businesses, and other electrical devices.
6. Any excess electricity generated by the solar panel can be stored in batteries for later use, fed and sold back into the grid or diverted into your DHW cylinder.










